
Content Menu
● Introduction to Disposable Plastic Plates
● The Manufacturing Process
● Detailed Insights into Each Manufacturing Step
>> Material Preparation
>> Extrusion Process
>> Thermoforming Techniques
>> Trimming and Finishing Touches
>> Quality Control Measures
● Environmental Impact of Disposable Plastic Plates
● Alternatives to Disposable Plastic Plates
>> Biodegradable Options Explained
● Consumer Awareness and Choices
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials are used to make disposable plastic plates?
>> 2. How long do disposable plastic plates take to decompose?
>> 3. Are there eco-friendly alternatives to disposable plastic plates?
>> 4. Can disposable plastic plates be recycled?
>> 5. What steps can I take to reduce my use of disposable plastic products?
● Citations:
Disposable plastic plates are ubiquitous in today's fast-paced world, providing convenience for a variety of occasions, from casual picnics to formal events. However, the journey from raw materials to the final product involves a complex manufacturing process that includes several stages. This article will explore in detail how disposable plastic plates are made, the materials involved, their environmental impact, and the alternatives available in the market.

Introduction to Disposable Plastic Plates
Disposable plastic plates are primarily made from two types of plastics: polystyrene and polypropylene. These materials are chosen for their lightweight nature, durability, and cost-effectiveness. The convenience of disposable plates makes them a popular choice for catering services, restaurants, and households. However, their single-use nature raises significant environmental concerns.
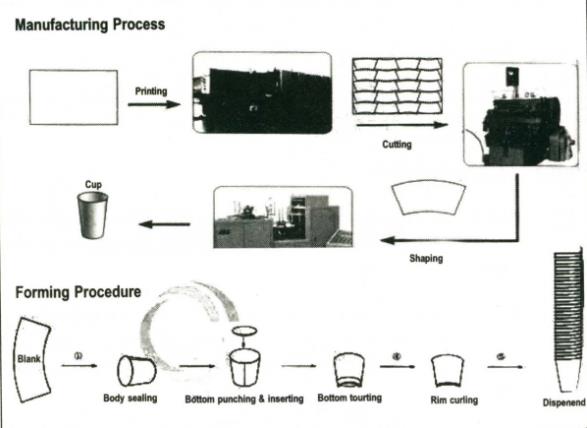
The Manufacturing Process
The production of disposable plastic plates can be broken down into several key steps:
1. Material Preparation
- The manufacturing process begins with the procurement of raw materials, typically polystyrene or polypropylene pellets. These pellets can be colored or clear, depending on the desired final product.
- The pellets are fed into an extruder machine where they are heated until they melt into a viscous liquid.
2. Extrusion
- The molten plastic is forced through a die to create a continuous sheet of plastic that is approximately two millimeters thick. This sheet is then cooled and prepared for further processing.
- During this phase, pigments may be added to create colored plates or to enhance visual appeal.
3. Thermoforming
- The cooled plastic sheet is reheated in an oven until it becomes malleable.
- It is then fed into a thermoforming machine that shapes the sheet into individual plates by pushing it into molds using vacuum pressure. This step is crucial as it determines the shape and depth of the plates.
4. Trimming and Finishing
- After forming, the plates are trimmed to remove excess material using a cutting machine.
- The trimmed edges are often recycled back into the production process to minimize waste.
5. Quality Control
- The finished plates undergo quality checks to ensure they meet safety and durability standards.
- Plates that do not meet these standards are discarded or recycled.
6. Packaging
- Finally, the plates are packaged in bulk for distribution to retailers or directly to consumers.
Detailed Insights into Each Manufacturing Step
Material Preparation
The choice of raw materials is critical in determining the properties of the final product. Polystyrene is widely used due to its excellent molding capabilities and low cost. It is lightweight yet strong enough to hold food without bending or breaking easily. Polypropylene, on the other hand, provides better heat resistance and is less likely to absorb food odors and flavors.
The preparation phase also includes quality checks on raw materials to ensure they meet industry standards before entering production.
Extrusion Process
The extrusion process is one of the most energy-intensive stages in manufacturing disposable plastic plates. Here's how it works:
- Heating: The extruder heats the plastic pellets until they reach a molten state.
- Shaping: The molten plastic is pushed through a die that shapes it into a flat sheet.
- Cooling: As the sheet exits the die, it is cooled down quickly using air or water sprays to solidify its shape.
This process can be adjusted based on the desired thickness and flexibility of the final product.
Thermoforming Techniques
Thermoforming can be categorized into several methods:
- Vacuum Forming: This involves heating the plastic sheet until it becomes pliable and then using a vacuum to pull it into a mold.
- Pressure Forming: In this method, air pressure is used to push the heated sheet against the mold, allowing for more intricate designs and features.
Both techniques ensure that each plate maintains uniform thickness and strength while achieving various designs suitable for different types of food service.
Trimming and Finishing Touches
Once formed, excess material around each plate must be trimmed off. This not only enhances aesthetics but also ensures safety by removing sharp edges.
The trimming process often involves automated machinery that cuts away excess plastic quickly and efficiently. Any leftover material from this step is ground down and reintroduced into the production cycle, promoting sustainability within manufacturing practices.
Quality Control Measures
Quality control is paramount in ensuring that every plate produced meets safety regulations and consumer expectations:
- Visual Inspections: Workers check for defects such as cracks or uneven surfaces.
- Strength Tests: Plates may undergo stress tests to evaluate their durability under various conditions (e.g., holding hot foods).
This rigorous quality assurance process helps maintain brand reputation and consumer trust.
Environmental Impact of Disposable Plastic Plates
The convenience offered by disposable plastic plates comes at a significant environmental cost:
- Resource Depletion: The extraction of fossil fuels for plastic production contributes to habitat destruction and climate change.
- Waste Generation: Disposable plastic plates contribute significantly to landfill waste as they can take hundreds of years to decompose. Unlike biodegradable materials, plastics break down into microplastics that can contaminate soil and water sources.
- Recycling Challenges: Although some plastics can be recycled, many disposable plates are made from low-grade plastics that are not accepted in curbside recycling programs.
Alternatives to Disposable Plastic Plates
As awareness of environmental issues grows, many consumers are seeking alternatives to traditional disposable plastic plates:
- Biodegradable Plates: Made from materials such as sugarcane bagasse or bamboo, these plates break down naturally and do not contribute to long-term waste.
- Recyclable Paper Plates: While not as durable as plastic options, paper plates made from uncoated paper can be composted if they do not contain harmful coatings.
- Reusable Dinnerware: For those looking to reduce waste significantly, investing in reusable dinnerware is an effective solution.
Biodegradable Options Explained
Biodegradable plates come in various forms:
1. Sugarcane Bagasse Plates: These are made from leftover fibers after sugar extraction. They are sturdy enough for hot foods and decompose within months when composted.
2. Bamboo Plates: Bamboo grows rapidly and can be harvested without killing the plant itself. Bamboo plates are durable and suitable for both hot and cold foods.
3. Palm Leaf Plates: Made from fallen palm leaves, these plates are entirely natural and biodegradable without any chemical additives.
4. Cornstarch-Based Products: PLA (polylactic acid) derived from cornstarch offers an alternative that breaks down more quickly than traditional plastics under composting conditions.
Consumer Awareness and Choices
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, their choices reflect a desire for sustainable options:
- Many restaurants now offer biodegradable or compostable tableware as part of their commitment to sustainability.
- Retailers have begun stocking eco-friendly products prominently to cater to this growing market segment.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of disposable plastic plates involves several steps from material preparation through quality control before reaching consumers' hands. While they offer convenience at events and everyday meals, their environmental impact cannot be overlooked. As consumers become more aware of these issues, exploring alternatives such as biodegradable or reusable options becomes essential for reducing our ecological footprint.

FAQ
1. What materials are used to make disposable plastic plates?
Disposable plastic plates are typically made from polystyrene or polypropylene, which are derived from fossil fuels.
2. How long do disposable plastic plates take to decompose?
Disposable plastic plates can take hundreds of years to decompose in landfills, contributing significantly to long-term waste issues.
3. Are there eco-friendly alternatives to disposable plastic plates?
Yes, biodegradable plates made from materials like sugarcane bagasse or bamboo offer sustainable alternatives that break down naturally without harming the environment.
4. Can disposable plastic plates be recycled?
While some plastics can be recycled, many disposable plastic plates are made from low-grade plastics that are not accepted in curbside recycling programs.
5. What steps can I take to reduce my use of disposable plastic products?
Consider using reusable dinnerware for everyday meals and special occasions, and explore biodegradable or recyclable options when disposables are necessary.
Citations:
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxN70ktR0jg
[2] https://www.thegoodboutique.com/inspiration/the-environmental-impact-of-disposable-tableware-and-sustainable-alternatives
[3] https://www.bambuhome.com/blogs/bambuliving/compostable-vs-disposable-plates
[4] https://techbullion.com/everything-you-need-to-know-what-are-disposable-plates-made-of/
[5] https://www.quitplastic.in/post/the-environmental-impact-of-traditional-disposable-tableware
[6] https://www.freshtableware.in/post/which-biodegradable-plates-and-cutleries-are-the-best-substitutes-of-the-plastic-ones
[7] https://customcupfactory.com/blogs/news/how-are-plastic-cups-made-understanding-the-process-of-disposable-cup-production
[8] https://smartyhadaparty.com/blogs/home/plastic-vs-paper-plates-which-is-better
[9] https://foogogreen.com/blog/ecofriendly-alternatives-for-paper-plates/
[10] https://www.greenalaskasolutions.com/pages/how-disposables-are-made

















