Content Menu
● 1. Overview of Disposable Cup Types
● 2. The Manufacturing Process of Paper Cups
>> Step 1: Sourcing Raw Materials
>> Step 2: Preparing the Paperboard
>> Step 3: Creating Cup Blanks
>> Step 4: Cup Forming
>> Step 5: PE Coating
>> Step 6: Printing and Design
>> Step 7: Cutting and Rim Rolling
>> Step 8: Quality Control and Packaging
● 3. The Manufacturing Process of Plastic Cups
>> Extrusion Process
>> Blow Molding Process
>> Thermoforming Process
● 4. Environmental Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials are used in making disposable paper cups?
>> 2. How long does it take to produce a disposable cup?
>> 3. Are disposable plastic cups recyclable?
>> 4. What is the difference between injection molding and thermoforming?
>> 5. How do manufacturers ensure quality control in cup production?
● Citations:
Disposable drink cups are an integral part of modern life, found in coffee shops, restaurants, and events worldwide. Understanding the manufacturing processes behind these cups reveals not only the complexity of their production but also the innovations aimed at sustainability. This article will delve into the detailed processes of making both paper and plastic disposable cups, highlighting the steps involved, materials used, and environmental considerations.

1. Overview of Disposable Cup Types
- Paper Cups: These are primarily used for hot beverages like coffee and tea. They are lightweight yet strong, often lined with a polyethylene coating to prevent leaks.
- Plastic Cups: Commonly utilized for cold drinks, plastic cups are made from various plastics, including polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP). They are favored for their durability and versatility.
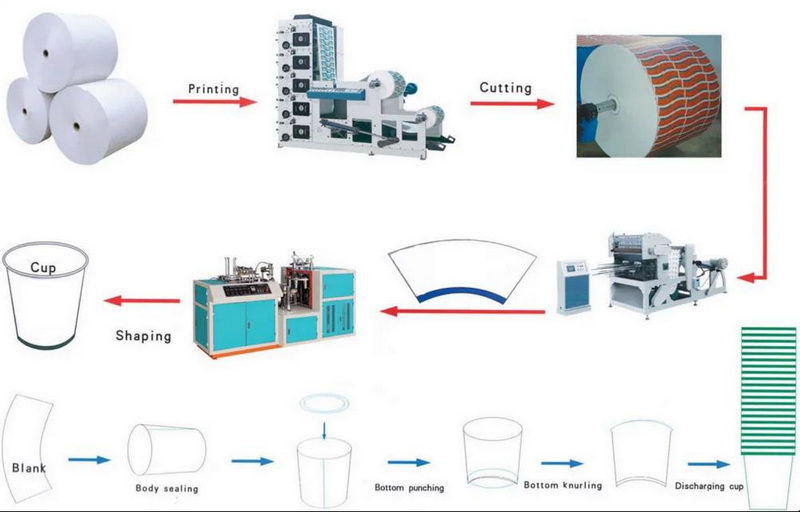
2. The Manufacturing Process of Paper Cups
The production of paper cups involves several key steps:
Step 1: Sourcing Raw Materials
The primary raw material for paper cups is paperboard, derived from pulped wood fibers. This material is selected for its strength and moisture resistance. The paperboard is often treated with a coating agent like polyethylene (PE) to enhance its leak-proof capabilities.
Step 2: Preparing the Paperboard
Once the raw materials are sourced, the paperboard undergoes a series of processes to make it suitable for cup production:
- Cleaning: Impurities are removed from the raw paperboard.
- Pulping: The paperboard is transformed into pulp, which is then bleached to achieve the desired whiteness or color.
Step 3: Creating Cup Blanks
The prepared paperboard is cut into circles known as "cup blanks." This process is performed using a cup-forming machine that ensures each blank is sized according to the desired cup volume.
Step 4: Cup Forming
In this stage, the cup blanks are shaped into cups through a series of intricate folding and sealing processes. Heat and pressure are applied to bond the edges securely.
Step 5: PE Coating
To ensure that the cups can hold liquids without leaking, a thin layer of PE coating is applied to the interior surface. This step is crucial for maintaining food safety standards.
Step 6: Printing and Design
Cups can be printed with various designs or logos using flexographic or offset printing techniques. This allows brands to customize their products according to consumer preferences.
Step 7: Cutting and Rim Rolling
After printing, excess paperboard is trimmed away, and the rims of the cups are rolled for comfort and structural integrity.
Step 8: Quality Control and Packaging
Before shipping, the cups undergo rigorous quality control checks to ensure they meet all specifications. Approved cups are then stacked, bundled, and packed for distribution.

3. The Manufacturing Process of Plastic Cups
Plastic cups are produced using various methods, primarily extrusion and molding techniques such as blow molding and thermoforming.
Extrusion Process
The manufacturing process begins with plastic granules:
- Heating Plastic Pellets: Plastic pellets are placed in an extruder where they are heated until they become molten. This transformation allows for easy molding.
- Forming the Sheet: The molten plastic is then pushed through a die, creating a continuous thick sheet.
- Cooling the Sheet: The sheet is cooled down to solidify it into a usable form.
Blow Molding Process
This method involves several steps:
- Creating Preforms: A small piece of plastic called a preform is made using injection molding.
- Heating the Preform: The preform is heated until it becomes soft and pliable.
- Blowing Air: The soft preform is placed into a blow mold where air is blown into it, causing it to expand and take shape.
- Cooling: After forming, the cup cools down to harden the plastic.
- Ejecting the Cup: Finally, it is removed from the mold and prepared for packaging or additional processing.
Thermoforming Process
Thermoforming is another common method used for making disposable plastic cups:
- Heating the Plastic Sheet: A flat sheet of plastic is heated until it becomes soft and flexible.
- Shaping the Cup: The heated sheet is placed over a mold that shapes it into a cup.
- In-Mold Cutting: Some processes use in-mold cutting to ensure precise edges while reducing waste.
- Cooling: After shaping, the plastic cools down to maintain its form.
- Stacking Solutions: Once cooled, cups can be stacked efficiently for packaging and storage.
4. Environmental Considerations
With growing environmental concerns regarding disposable products, manufacturers are exploring sustainable alternatives:
- Biodegradable Materials: Some companies are developing biodegradable plastics made from natural materials like cornstarch or sugar cane. These materials decompose more easily than conventional plastics.
- Recycling Programs: Many manufacturers have initiated recycling programs to reduce waste associated with disposable cup production. Efforts include creating closed-loop systems where leftover materials from production are reused in new products.
Conclusion
The production of disposable drink cups—whether made from paper or plastic—involves intricate processes that combine technology with material science. As consumer awareness regarding environmental issues continues to rise, manufacturers face increasing pressure to innovate and adopt more sustainable practices. By understanding these processes better, consumers can make informed choices about their use of disposable products.

FAQ
1. What materials are used in making disposable paper cups?
Disposable paper cups primarily use paperboard as the main material, which is coated with polyethylene (PE) for waterproofing.
2. How long does it take to produce a disposable cup?
The manufacturing process can take as little as one minute per cup once all materials are prepared.
3. Are disposable plastic cups recyclable?
Yes, many disposable plastic cups made from PET or PP can be recycled; however, proper recycling facilities must be available.
4. What is the difference between injection molding and thermoforming?
Injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into molds while thermoforming uses heated sheets of plastic shaped into molds.
5. How do manufacturers ensure quality control in cup production?
Manufacturers conduct rigorous inspections at various stages of production to ensure that all cups meet safety and quality standards.
Citations:
[1] https://inochiglobal.com/how-are-plastic-cups-manufactured/
[2] https://greenfeel.co.uk/blog/info/how-paper-cups-are-made-manufacturing-process-quality-control
[3] https://topcupfactory.com/how-are-plastic-cups-made/
[4] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxN70ktR0jg
[5] https://www.limepack.eu/blog/paper-cups-en/the-process-of-manufacturing-of-paper-cups
[6] https://customcupfactory.com/blogs/news/how-are-plastic-cups-made-understanding-the-process-of-disposable-cup-production
[7] https://disposableamerica.org/course-projects/a-wholesome-drink/section-ii-what-goes-into-a-dixie-cup-paper-cup-manufacturing/

















